With the extensive library of domains and webpages across the world wide web, you might think the internet is running on words. But the reality is that the sentences you write and read online have nothing to do with how your computer navigates the endless web pages of the internet.
When you enter a website address in your browser, you're not actually telling your computer the physical location of the website. Computers only understand numbers, so the URL you type is only useful to the humans who are using the computer.
To make sense of words, computers rely on Domain Name System (DNS) server to translate the URL into the actual IP address of the website's server.

These servers come in all shapes and sizes and are central to how the internet works and how you navigate from page to page.
What is a DNS server?
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is a framework of internet infrastructure that translates domain names into numerical IP addresses that computers can understand.
It’s basically the phone book of the internet, turning domain names like Google.com or YouTube.com into IP addresses that devices need to load internet resources and identify each other on a network.
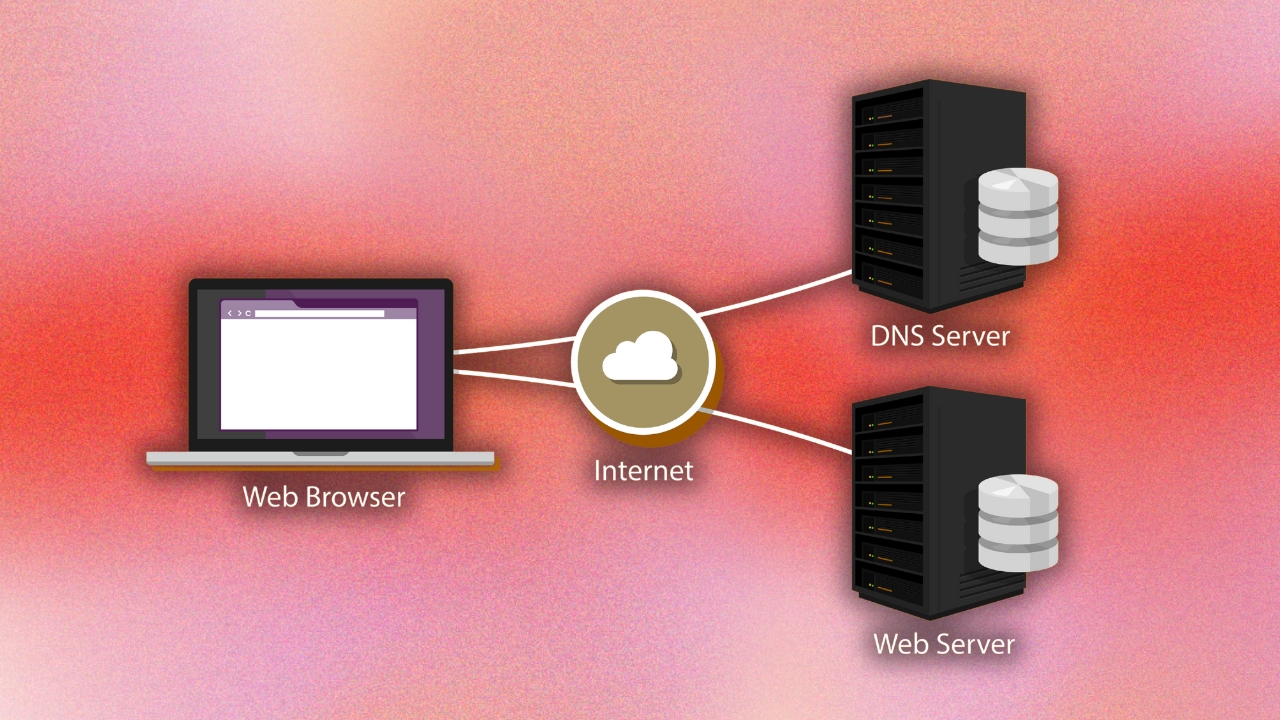
DNS servers help people navigate the internet by converting easily memorable domain names into the numerical language that computers and network devices can read ( like 99.74.225.74). to send people to the correct web page.
There are many different DNS servers, and you can choose which one to use. Some popular options include Google Public DNS and Cloudflare DNS, but there are many different options out there to suit your needs.
How do DNS Servers Work?
When you enter a website address in your browser, your computer doesn’t understand the domain name, so it sends a query to a DNS server. This server could be one provided by your internet service provider (ISP), or one you've chosen yourself.
The DNS server has a massive database that maps domain names to IP addresses. It searches its database for the IP address associated with the domain name you entered.
Once the DNS server finds the IP address, it sends it back to your computer. Now that your computer knows the website's IP address, it can use that to establish a connection and send and receive data, allowing you to view the website.
Why change to a public DNS?
1. Speed
Public DNS servers are often faster than ISP servers, especially if you're far from your ISP's servers. This is because public DNS servers have a larger network of servers distributed around the world. Large public DNS providers often invest heavily in their infrastructure, using high-speed connections and powerful hardware to handle a large volume of requests efficiently.

When SOAR Redefines Defense
Boards are backing SOAR to turn fragmented tools into coordinated, automated response and shrink breach impact windows across the enterprise.
2. Reliability
Public DNS servers are generally more reliable than ISP servers. If your ISP's DNS server is overloaded or having technical difficulties, you may experience slow browsing speeds or be unable to access websites altogether. Public DNS providers, however, often have built-in redundancy within their networks. This means if one server goes down, others can pick up the slack and continue resolving DNS requests.
3. Security
Public DNS servers offer security features that can help protect you from malware and phishing attacks. By using a separate entity for DNS resolution, you're potentially reducing the attack surface for your ISP to tamper with your internet experience.
Some servers also support DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), which digitally signs DNS records making it harder for attackers to tamper with them and redirect you to malicious websites. Not all ISPs or public DNS servers offer this yet, so check the provider's information.
4. Privacy
Many public DNS providers have a stronger focus on privacy and don't log your browsing history. But it’s important to note that your ISP can still see what websites you visit, even if you're using a public DNS server. This is because your ISP can see the traffic going to and from your device. To prevent this, many people use proxy servers to hide their IP addresses and keep their personal information private.
Inside the New Blockchain Stack
See how MPC custody, SIEM-integrated on-chain monitoring and off-exchange settlement are reshaping enterprise blockchain controls.

5. Content Control
Many public DNS providers offer content filtering options, allowing you to block specific categories of websites, which can be useful for parental control.
Best DNS Servers for 2024
There is a range of both public and private DNS servers available today, each with its own set of features, speeds and methods for helping you navigate the web as efficiently as possible.
In this top 10, we’re counting the best DNS servers for 2024. We’ll compare their speed, reliability and security so you can choose the best DNS settings for your needs.







Comments ( 0 )