
With cyber incidents on the rise around the world, keeping your data secure has never been more important in 2023. Cyber attacks can devastate your business, leaving your reputation in tatters and your users at risk of further attacks once their data is compromised.
There are a variety of different tools available to detect incidents and dampen their impact when they happen. One of these essential tools is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS), which allows companies to identify security breaches in an instant so that they can create a response plan when they happen.
But what are intrusion detection systems, and how do they work? This article delves deep into the meaning of an intrusion detection system, exploring its types while giving real-world examples of IDS solutions.
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)? Definition
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a security system that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and generates alerts when such activity is discovered.
The primary goal of an IDS is to detect and respond to potential security threats, breaches, or vulnerabilities. These systems act as digital sentinels, tirelessly watching over your network, and alerting administrators or automated systems when suspicious or malicious behavior is detected.
How does an IDS work?
IDSes work by analysing network traffic patterns and comparing them to known attack signatures or deviations from normal behaviour. When an IDS detects suspicious activity, it generates an alert that can be sent to a security administrator or logged for later review.
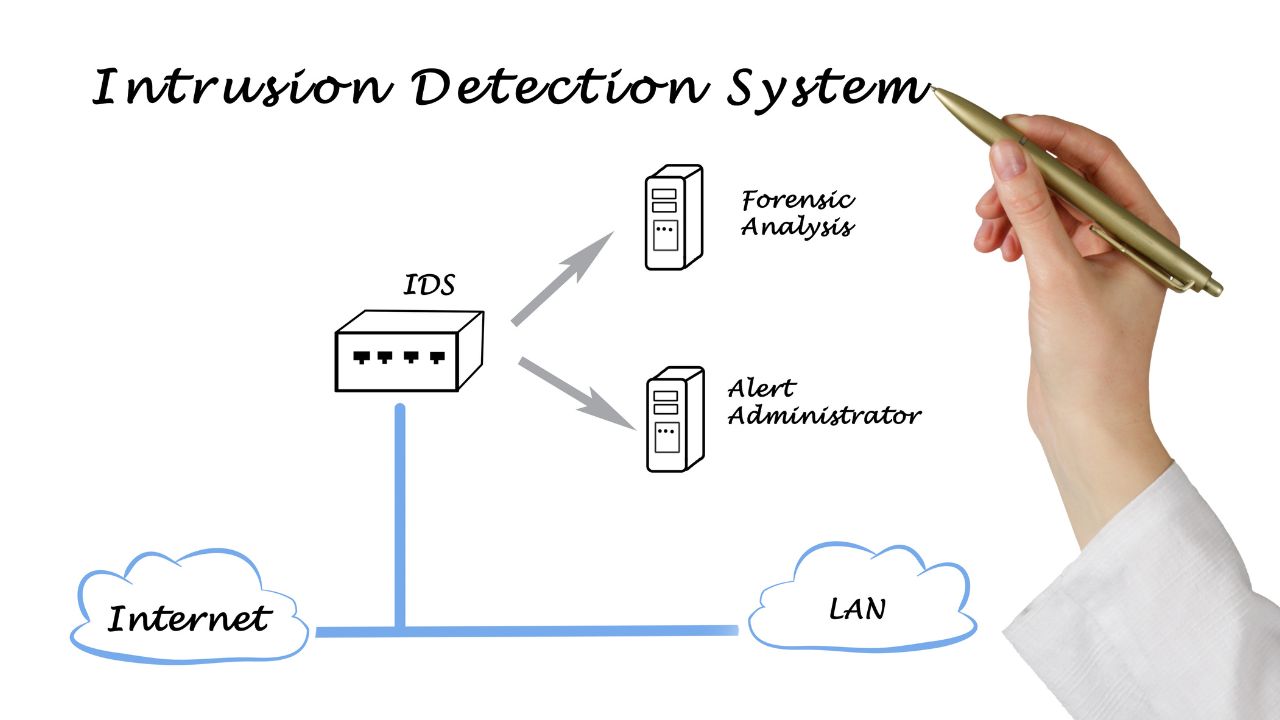
Here is a step-by-step guide of how an IDS might work to detect a network attack:
- The IDS monitors all network traffic passing through a specific device, such as a firewall or router.
- The IDS compares the network traffic against a database of known attack signatures.
- If the IDS detects a match, it generates an alert.
- The alert is sent to a security administrator, who can investigate the potential attack and take appropriate action.
IDSs can be deployed on a variety of devices, including routers, firewalls, servers, and endpoint devices. They can also be deployed in the cloud.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
While there are a variety of different types of intrusion detection systems on the market, they are generally classified by their deployment location:
- Network-based intrusion detection systems (NIDSes) are deployed on network devices, such as routers and firewalls. They monitor all traffic that passes through the device and generate alerts when they detect suspicious activity.
- Host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDSes) are deployed on individual computers or servers. They monitor the activities of the computer or server and generate alerts when they detect suspicious activity.
As well as their deployment location, intrusion detection systems can also be classified based on signature detection and anomaly detection:
- Signature-based IDSes detect suspicious activity by looking for known attack patterns. These patterns are typically stored in a database of attack signatures. When an IDS detects a pattern that matches a signature in the database, it generates an alert.
- Anomaly-based IDSes detect suspicious activity by looking for deviations from normal behaviour. These systems establish a baseline of normal behaviour for the network and then generate alerts when they detect activity that deviates from the baseline.
Some IDSes use a combination of signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods. These hybrid IDSes are often more effective at detecting both known and unknown attacks.
Examples of Intrusion Detection Systems
There are many different examples of intrusion detection systems on the market today, each of which offers a number of benefits that can help keep your business secure. Here are some examples of intrusion detection systems on the market today:
1. Snort - Snort is a free and open-source network intrusion detection system (NIDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS). It is one of the most popular IDSes in the world and is used by organizations of all sizes to protect their networks from attack.
Snort uses both signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods. Signature-based detection involves looking for known attack patterns in network traffic. Anomaly-based detection involves looking for deviations from normal behaviour in network traffic Snort is a very versatile IDS, and can be used to detect a wide range of attacks, including:
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks
- Port scans
- Malware infections
- Network probes
- Data breaches
Snort is a powerful tool, but it can be complex to configure and manage. It’s important to have a good understanding of network security before using Snort.
2. Suricata - Suricata is a free and open-source network intrusion detection system (NIDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS). It is a fork of Snort, and shares many of the same features. However, Suricata also includes a number of improvements over Snort, such as:
- Faster performance
- More efficient memory usage
- Better support for multi-threaded processing
- Enhanced anomaly detection capabilities
Suricata is a good choice for organisations that need a high-performance IDS/IPS solution.
3. OSSEC - OSSEC is a free and open-source host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS). It can be used to monitor the activities of individual computers or servers and generate alerts when it detects suspicious activity.
OSSEC uses a variety of detection methods, including:
- File integrity monitoring
- Log monitoring
- Rootkit detection
- Process monitoring
OSSEC is a good choice for organizations that need to monitor the security of their individual computers or servers.
4. Nagios - Nagios is a free and open-source network monitoring and intrusion detection system. It can be used to monitor the availability and performance of network devices and services. Nagios can also be used to detect suspicious activity on the network.
Nagios is a good choice for organizations that need a comprehensive network monitoring and intrusion detection solution.
5. Splunk - One of the most popular security solutions in the world, Splunk's SIEM system can be used to collect and analyse data from a variety of security devices, including IDSes. Splunk can also be used to generate alerts and reports.
Splunk is a good choice for organizations that need a powerful IDS system to help them manage their security data.
Benefits of intrusion detection systems
Implementing an intrusion detection system (IDS) can offer a number of benefits to organizations of all sizes, including:
- Early Threat Detection - An IDS provides early detection of potential security threats. By identifying malicious activities in their infancy, organizations can respond promptly, mitigating the potential damage and minimizing the cost of recovery.
- Improved Network and System Security -An IDS enhances the overall security posture of a network or system. It acts as an additional layer of protection, complementing firewalls, antivirus software, and other security measures, thereby reducing the risk of successful attacks.
- Reduced Downtime and Data Loss - Prompt detection of threats means quicker response times, reducing network downtime and preventing data breaches. Preventing or minimizing the impact of a breach can save an organization substantial time and resources.
- Protection from Zero-Day Attacks - Anomaly-based IDSs are effective against zero-day attacks. These attacks target vulnerabilities that are not yet known or patched. By monitoring for unusual behaviour rather than relying on known signatures, an IDS can detect such attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance - Many industries have strict regulatory requirements for data security. Implementing an IDS can help organizations meet these requirements and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
- Enhanced Incident Response - When an IDS detects a potential threat, it provides valuable information for incident response. It can alert administrators with information on the nature of the attack, affected systems, and the extent of the breach, enabling a swift and targeted response.
- Real-Time Monitoring - An IDS continuously monitors network and system activities in real time, ensuring that threats are identified and addressed as they occur.
- Versatility - IDSs can be configured to suit the specific needs of an organization. They can be tailored to monitor for specific types of attacks or vulnerabilities, making them highly adaptable to different environments.
Overall, implementing an IDS can be a valuable investment for organizations of all sizes. IDSes can help organisations protect themselves from a wide range of threats, improve their security posture, and comply with security regulations.
How to choose an IDS
When choosing an IDS, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of your organisation. Some factors to consider include.
- Type of IDS: Determine whether a network-based or host-based IDS is more suitable for your environment.
- Scalability: Ensure the IDS can scale with your organization's growth.
- Customization: Look for systems that can be configured to match your specific security needs.
- Integration: Consider how the IDS will integrate with your existing security infrastructure, such as firewalls, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, and antivirus solutions.
- Vendor Reputation: Choose a reputable vendor with a history of delivering effective IDS solutions.
- Support and Updates: Ensure the vendor provides regular updates and support for the IDS.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including not only the initial investment but also ongoing maintenance and operational costs.
Final thoughts
IDS technology is constantly evolving as new threats emerge. IDSs are becoming more sophisticated and capable of detecting a wider range of attacks. IDSs are also becoming more integrated with other security solutions, such as firewalls and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Regardless IDSs will likely continue to represent an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy. Properly implementing an IDS can help your organisation protect itself from a wide range of threats, improve its security posture, and comply with security regulations.












